Build Instructions
Complete step-by-step guide to building your Rep5x 5-axis printer
These are the same build instructions available on GitHub, but formatted for easier reading on the web. Want to improve these instructions? Open a PR on GitHub — we'd love your help! Need support? Join our Discord community!
Select Your Printer Model (Optional)
Below you'll find the universal build instructions that work for all printers. To see printer-specific instructions and bill of materials, select your printer model:
BOM
Universal BOM
Universal components required for any Rep5x 5-axis printer conversion. These parts are compatible across all supported printer models.
Universal 3D printed components
All files available in ../3d-printed-parts/current/3mf/.
Recommended material: PETG for all components.
| Component | File | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C-driven-pulley | C-driven-pulley_v1.1.0.3mf | Drive pulley for C-axis |
| B-driven-pulley | b-driven-pulley_v1.1.0.3mf | Custom pulley for B-axis drive |
| B_arm | B_arm_v1.0.0.3mf | Rotational arm for B-axis |
| Slip ring holder | slip-ring-holder_v1.1.1.3mf | Mount for slip ring assembly |
| Spacer 3mm | spacer-3mm_v1.0.0.3mf | 3mm spacer component |
| Hotend spacer | hotend-spacer_v1.0.0.3mf | Spacer for hotend mounting |
Universal COTS components
| Qty | Part Number | Description | Notes | Purchase links |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Nema17 stepper motor | Stepper motors for C and B axis | Standard 42mm body | AliExpress Amazon |
| 2 | GT2 20T 5mm bore | Drive pulleys for C and B axis | 20 teeth, 5mm bore | AliExpress Amazon |
| 1 | GT2 timing belt 6x188mm | Drive belt for C-axis | 6mm wide, 188mm length | AliExpress Amazon |
| 1 | GT2 timing belt 6x158mm | Drive belt for B-axis | 6mm wide, 158mm length | AliExpress Amazon |
| 2 | 608 2RS bearing DIN625 | Ball bearings for B-axis rotation | Standard skateboard bearings | AliExpress Amazon |
| 2 | 61804 bearing | Thin section bearing for carriage mount | For C-axis rotation | AliExpress Amazon |
| 1 | Microswitch | Endstop switch for B-axis | 2-pin micro limit switch | AliExpress Amazon |
| 1 | Optical sensor | C-axis homing sensor | 3-pin optical endstop sensor | AliExpress Amazon |
| 1 | Control board | 6+ stepper driver board | See tested control boards section | AliExpress Amazon |
| 6 | TMC2208 | Stepper drivers | UART mode, for all 6 axes | AliExpress Amazon |
| 1 | MST-005-12A slipring | Slipring assembly | 12 channels, 2A each, 5mm bore | AliExpress Amazon |
| 1 | Wire/cables | Connection wires | For slip ring and stepper connections | - |
| 1 | JST connectors (optional) | Removable connectors | For easy maintenance | AliExpress Amazon |
| 1 | Cable organizers (optional) | Zip ties, cable clips, or spiral wrap | For clean wire routing | - |
Universal fasteners
| Qty | Description | Purchase links |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | DIN912 M3x6mm socket head cap bolt | AliExpress Amazon |
| 8 | DIN912 M3x10mm socket head cap bolt | AliExpress Amazon |
| 2 | M3 heat-set insert for plastic | AliExpress Amazon |
Electronics requirements
Control board requirements
- Minimum stepper drivers: 6 (X, Y, Z, E, A, B)
- Processor: 32-bit ARM recommended
- Communication: USB, UART support
- Power: 24V DC input capability
Tested control boards
- BTT Octopus V1.1 (STM32F446ZE) - 8 stepper drivers, proven working
Stepper drivers
- Required: 6x TMC2208 (UART) or equivalent
- Configuration: X, Y, Z, Extruder, C-axis, B-axis
- Benefits: Unified driver type simplifies wiring and configuration
Component specifications
Slipring (MST-005-12A)
- Channels: 12 electrical channels
- Current rating: 2A per channel
- Through-bore: 5mm diameter
- Purpose: Allows continuous rotation
Printer-specific components
The following components require printer-specific adaptation:
- Carriage mount - Varies by printer X-carriage design
- Endstop positions - May require relocation or addition
See printer-specific folders for adaptation requirements.
Assembly instructions
Universal assembly instructions
Complete build instructions for converting any compatible 3D printer to 5-axis capability. Based on proven build process from working prototypes.
Throughout this guide you'll find affiliate links to components. Purchases through these links support the Rep5x project development and help keep the project open source.
Before you start
Important: Read through this entire document before beginning assembly. This will help you understand the complete process, identify any missing components, and plan your build timeline effectively.
Contributing improvements
If you discover easier methods, better techniques, or have suggestions for improvement during your build, please contribute back to the project:
- Open a Pull Request on GitHub with your proposed changes
- Document your improvements with photos and clear explanations
- Share your experience in our Discord community
- Help make Rep5x better for everyone!
Prerequisites
Tools required
- 3D printer - For printing Rep5x components
- Hex keys - M2.5, M3 sizes (long hex key needed for C-axis stepper installation)
- Wire strippers and connecting tools - For wire connections (crimping tools if using JST, soldering iron if soldering)
- Multimeter - For electrical testing
- Computer - For firmware flashing and calibration
Skills required
- Basic 3D printing - Print settings and quality control
- Basic electronics - Wiring and wire connections (soldering or crimping)
- Firmware flashing - Arduino IDE or VSCode with PlatformIO
- Mechanical assembly - Heat insert installation, bearing installation
Time estimate
- Electronics preparation: 4-6 hours (board flashing, testing, slip ring prep)
- Component preparation: 2-3 hours (steps 5-9)
- Mechanical assembly and installation: 4-6 hours (steps 10-14)
- Final testing and calibration: 2-4 hours (step 15)
- Total: 12-19 hours over several days
Part 1: Electronics preparation
Step 1: Gather all materials
Verify you have all components from:
- Universal BOM - All shared components
- Printer-specific BOM - Additional printer-specific components
- 3D printed parts - All components printed and quality checked
Step 2: Flash your control board
Download firmware configuration
Download the Marlin firmware configuration from your printer-specific folder: Find your printer's firmware config
Flash firmware
- Download Marlin 2.1.x from official repository
- Replace configuration files with Rep5x versions
- Compile and upload to control board
- Verify upload successful via serial connection
Step 3: Remove old control board
- Power down printer completely
- Disconnect all cables from old control board
- Remove old board from electronics enclosure
Step 4: Install new control board and test basic functions
Install control board
- Place new board next to your printer
- Set all jumpers correctly according to the wiring diagram for your control board
- Install TMC2208 drivers in all 6 positions (X, Y, Z, E, A, B)
- Connect all printer components (steppers, end-stopsm , heated bed, thermistors, hot-end etc.)
- Connect power supply and verify 24V input
Test all components work correctly
Test each component with G-code commands:
Motors (movement test):
G28 ; Home all axes
G1 X100 ; Test X motor
G1 Y100 ; Test Y motor
G1 Z50 ; Test Z motor
G1 E10 ; Test extruder motor
G1 C10 ; Test C-axis motor (yaw rotation)
G1 B10 ; Test B-axis motor (tilt rotation)
Heated bed:
M140 S60 ; Set bed temperature to 60°C
M105 ; Check temperatures
M140 S0 ; Turn off bed heater
Hotend:
M104 S180 ; Set hotend to 180°C
M105 ; Check temperatures
M104 S0 ; Turn off hotend
Thermistors:
M105 ; Read all temperatures - should show room temperature
Endstops:
M119 ; Check all endstop status - should show current state
Important: All basic printer functions must work before proceeding.
Part 2: Component preparation
Step 5: Prepare slip ring with wire connections
Slip ring wiring requirements
The slip ring needs the following connections:
- 1x 4-pin connection - For B-axis stepper motor
- 4x 2-pin connections - For: hotend fan, hotend heater, hotend thermistor, B-axis endstop
Wire connection preparation
- Cut wires to appropriate lengths for routing through slip ring (or keep full length for safety - prevents wires being too short, though cable management is harder)
- Connect wires using your preferred method:
- JST connectors (recommended) - Clean, removable connections
- Direct soldering - Permanent but reliable, no prep needed for now
- Wire nuts or terminal blocks - Alternative connection methods
- Test continuity of all connections using a multimeter
Note: JST connectors are not required but preferred over permanent soldering for easier maintenance and troubleshooting.
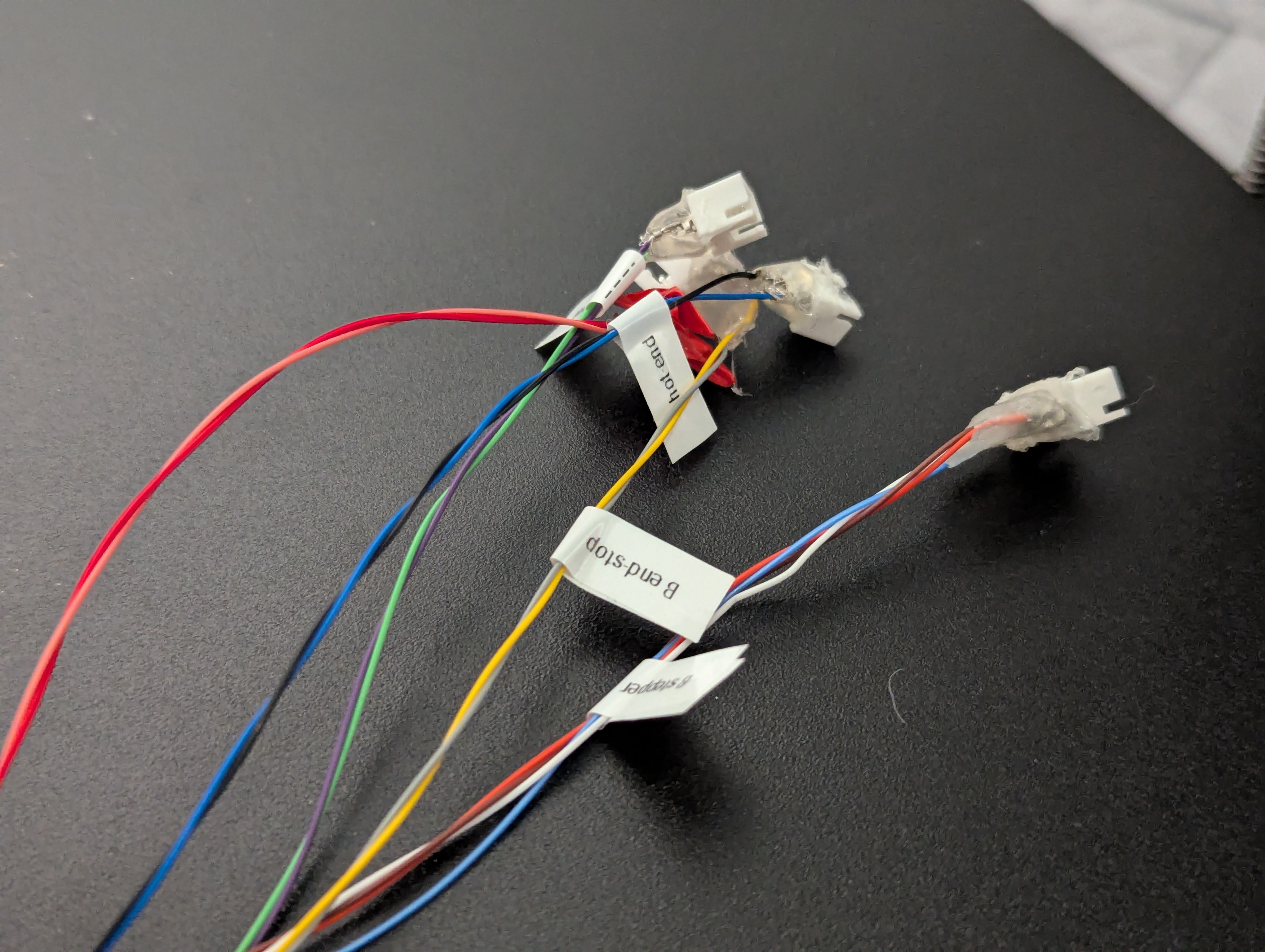
Figure 1: Slip ring prepared with JST connectors for easy connection and disconnection
Step 6: Prepare B-driven-pulley
Heat insert installation
- Install 2x M3 heat-set inserts in B-driven-pulley
- Install M3x10 socket head bolt in one insert
- Adjust bolt position - should stick out slightly to trigger microswitch endstop
- Test fit - bolt should protrude ~1-2mm for reliable endstop triggering
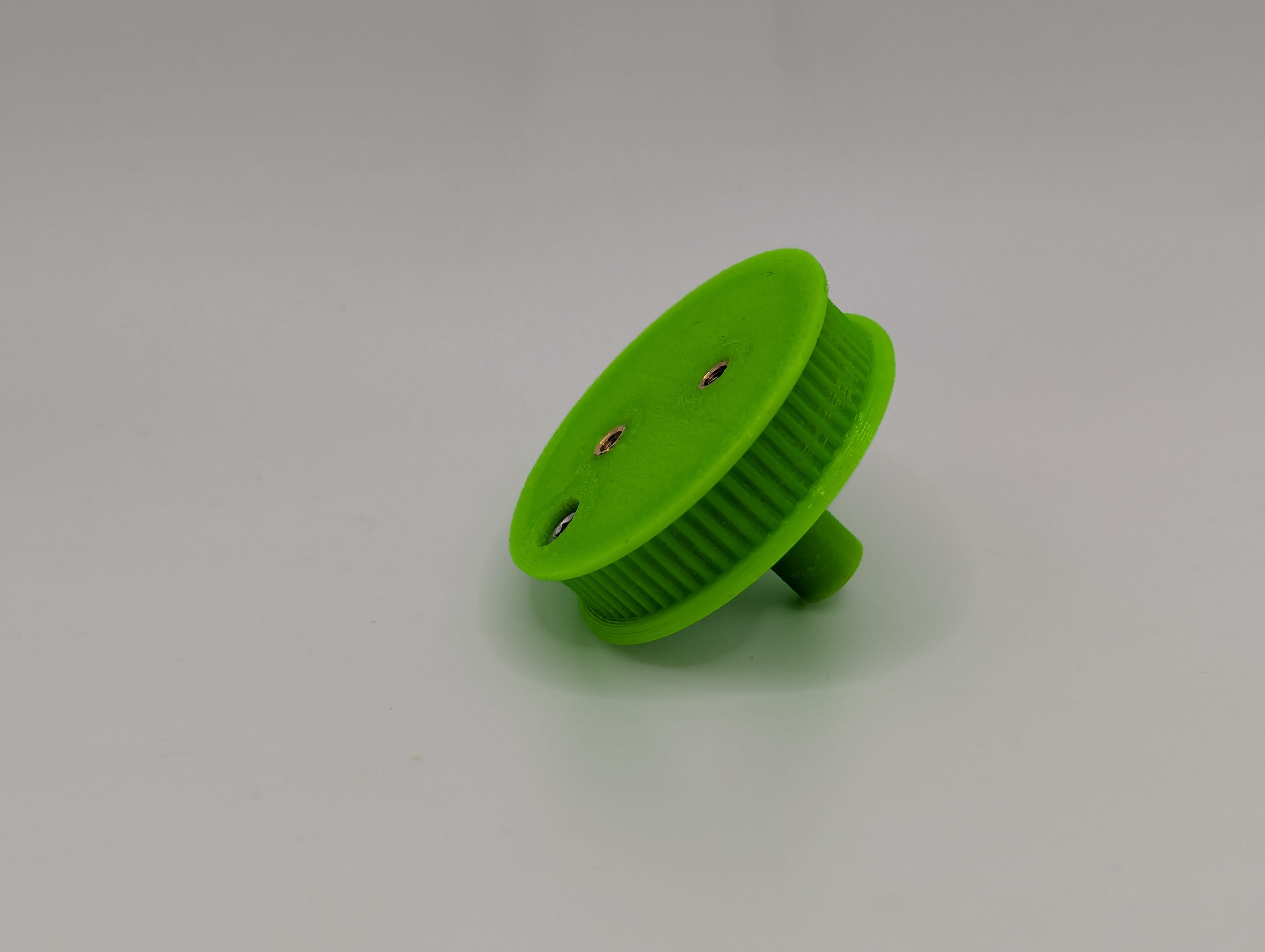

Figure 2: B-driven-pulley with heat-set inserts and endstop trigger screw installed
Step 7: Install bearings in B_arm
Bearing installation
- Install 2x 608 bearings in B_arm bearing pockets
- Press fit carefully - bearings should sit flush and rotate smoothly
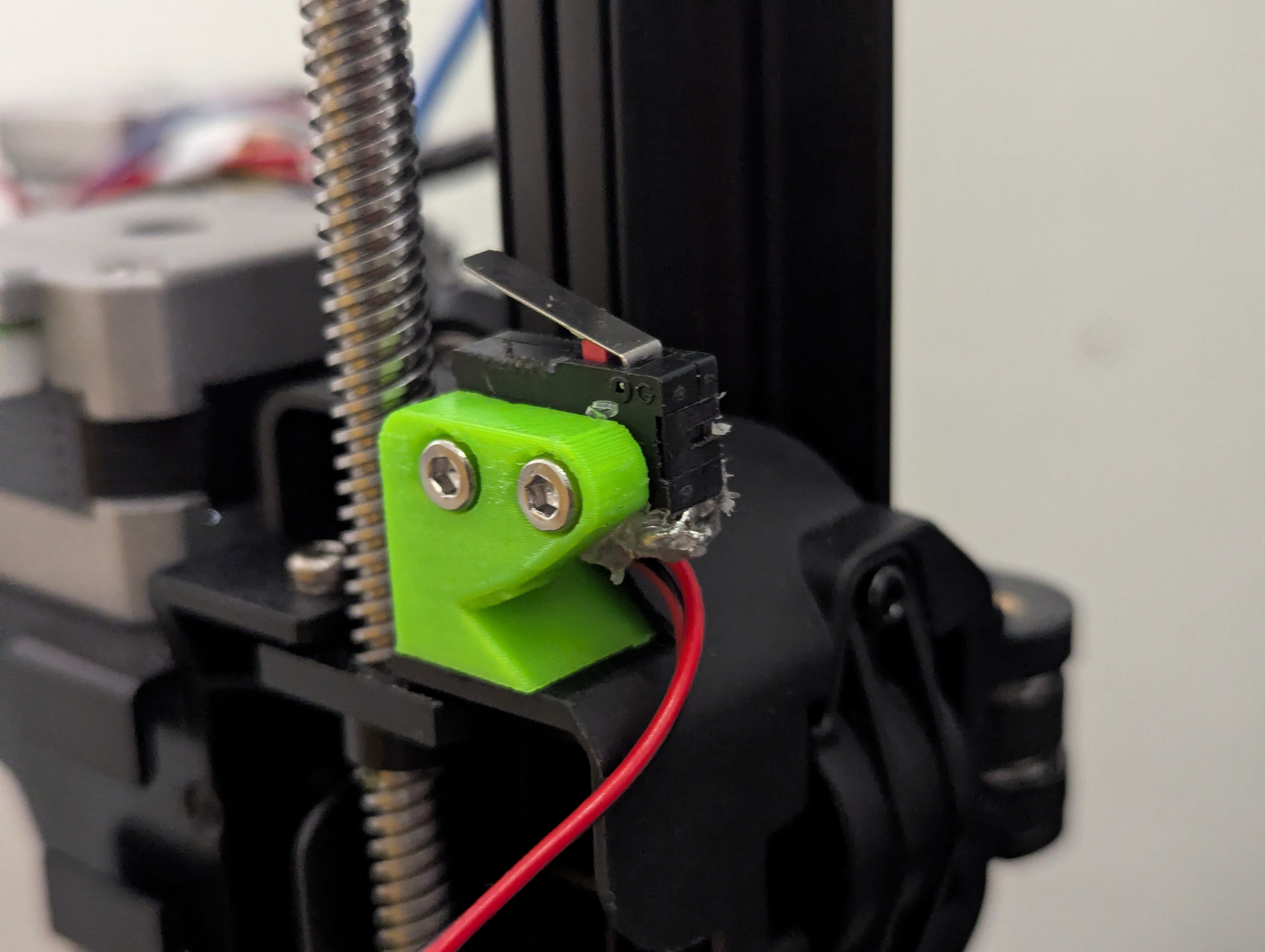
Step 8: Install and position microswitch in B_arm
Microswitch preparation
- Install microswitch in B_arm mounting location
- Trim or remove metal actuator needed for proper positioning
- Test position - Install B-driven-pulley temporarily and check when screw clicks microswitch
- Find sweet spot - Adjust for reliable triggering without interference
- Secure with hot glue once optimal position found
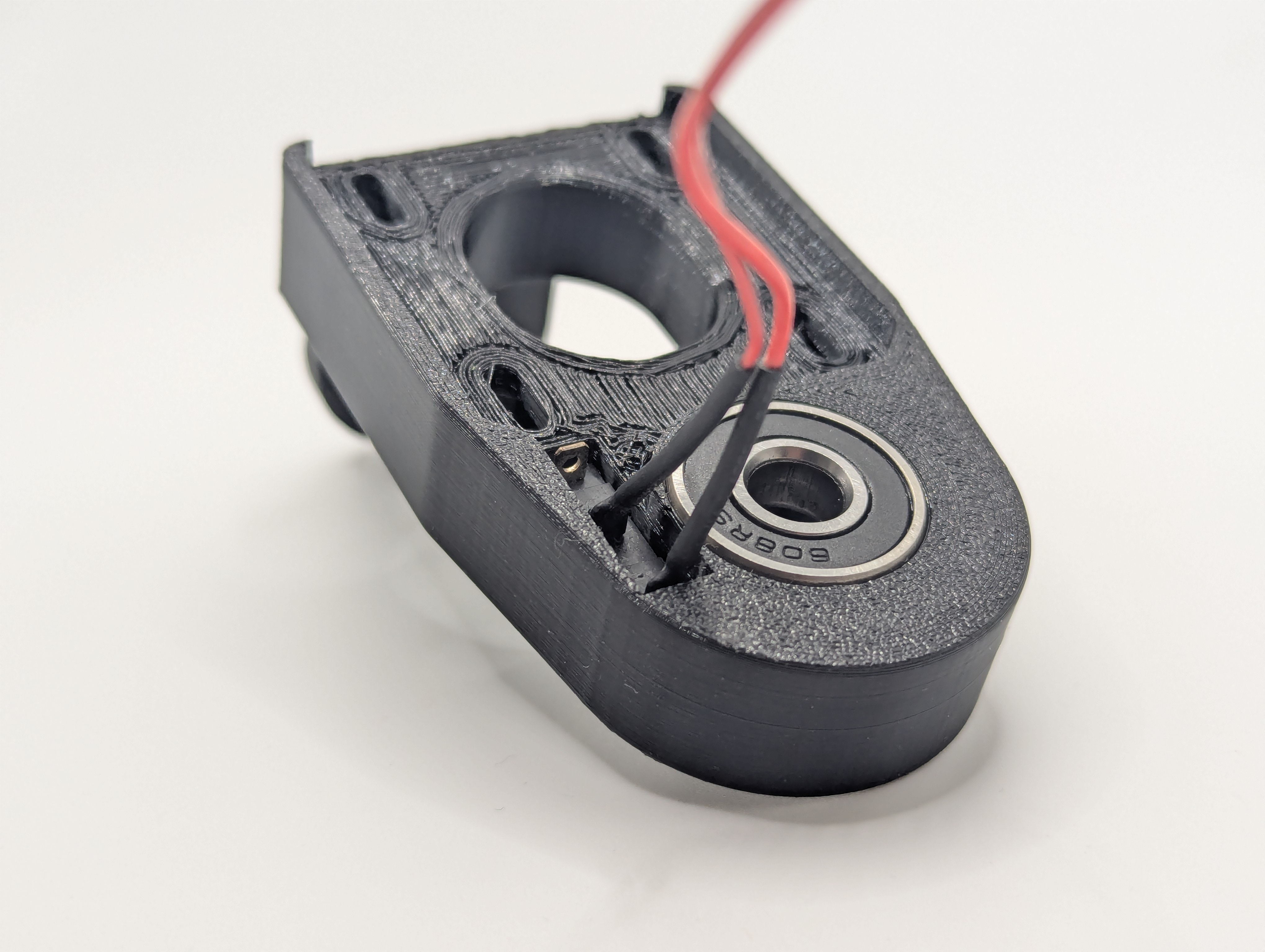

Figure 3: B_arm assembly showing installed bearings and positioned microswitch
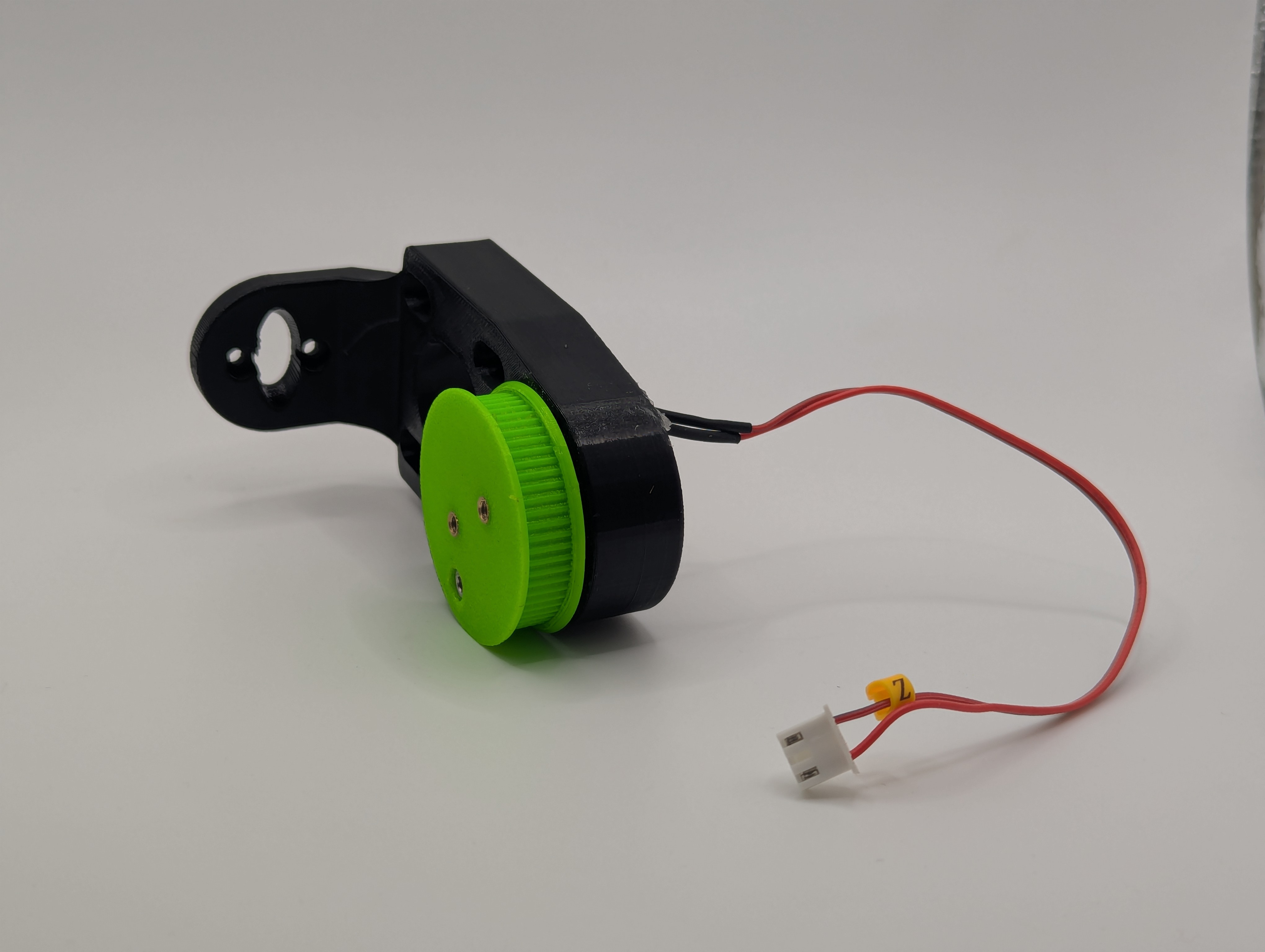
Figure 4: B_arm connected to B-driven-pulley, showing complete tilt mechanism
Step 9: Prepare carriage mount
Bearing installation
- Install 2x 61804 bearings in carriage mount
- Verify smooth rotation and proper seating
Note: Do not install the C-driven-pulley yet - this must be done after attaching to the printer since the pulley blocks access to mounting screws on some printers like the Ender 3 V3 SE.
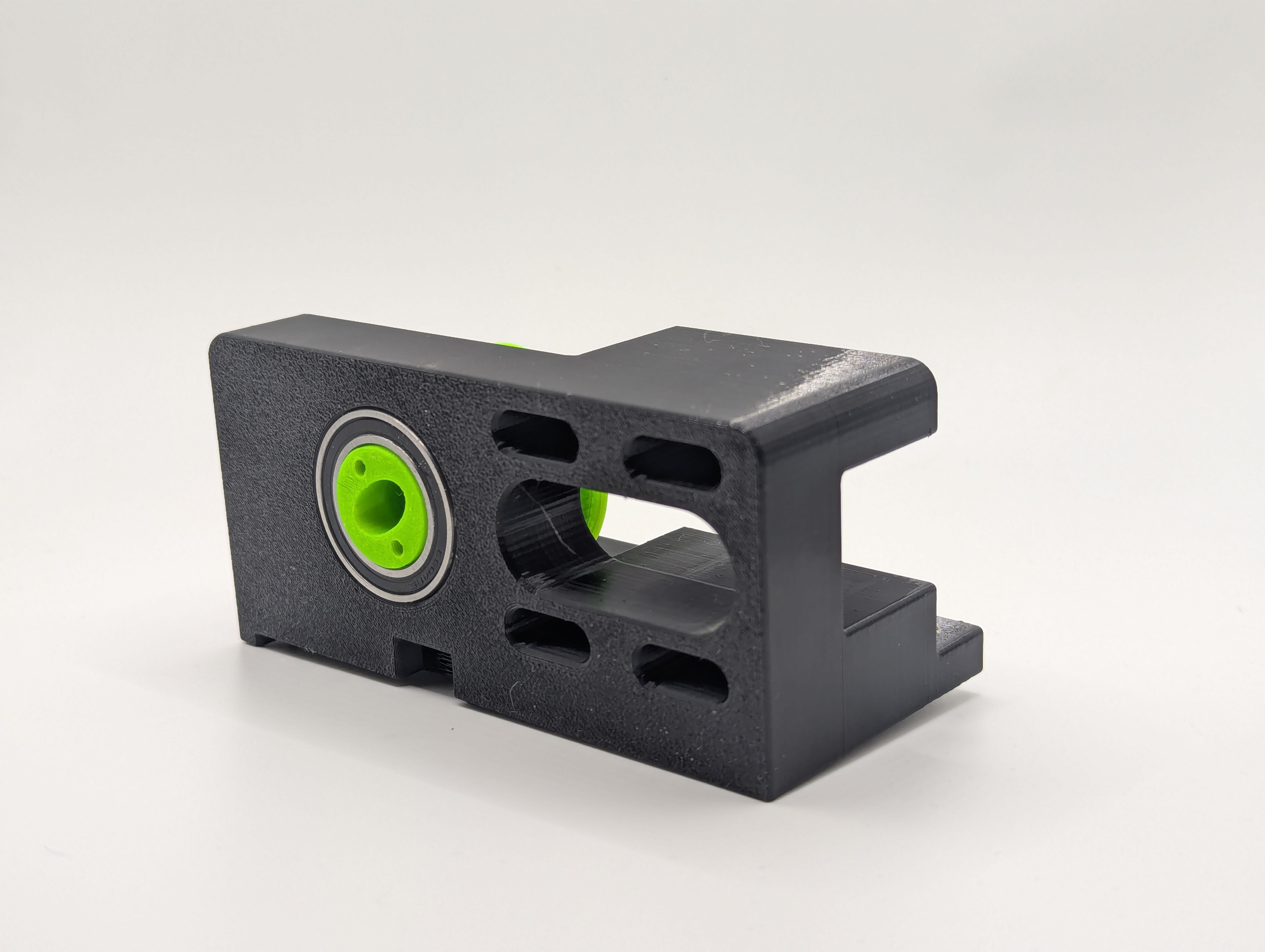

Figure 5: Carriage mount with 61804 bearings installed - ready for mounting to printer
Part 3: Installation on printer
Step 10: Install carriage mount to X-axis
Carriage mount installation
- Remove original hotend assembly from printer
- Attach carriage mount to X-carriage using original mounting screws
- Verify clearance with frame and motion systems
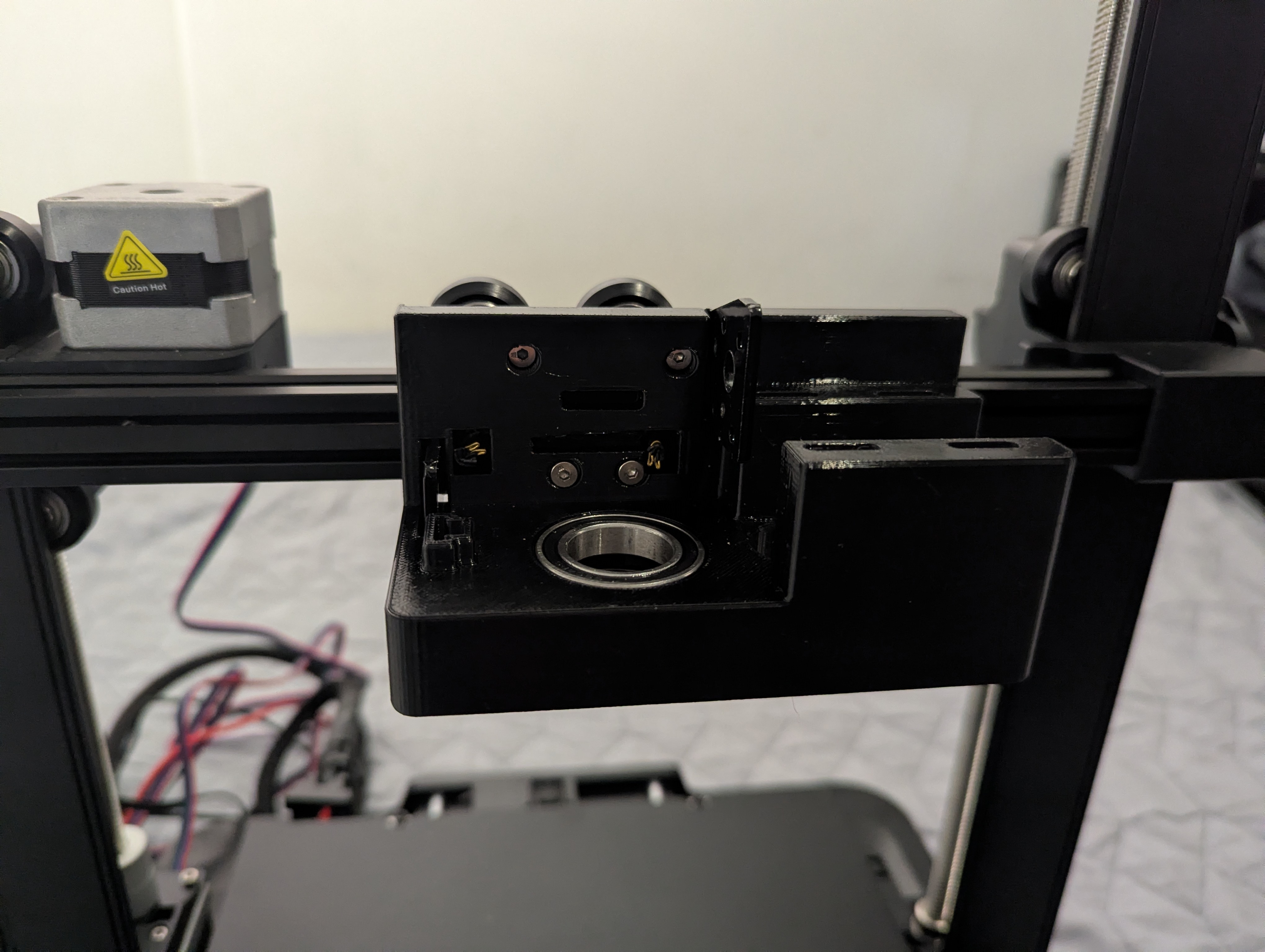
Figure 8: Carriage mount attached to printer's X-carriage
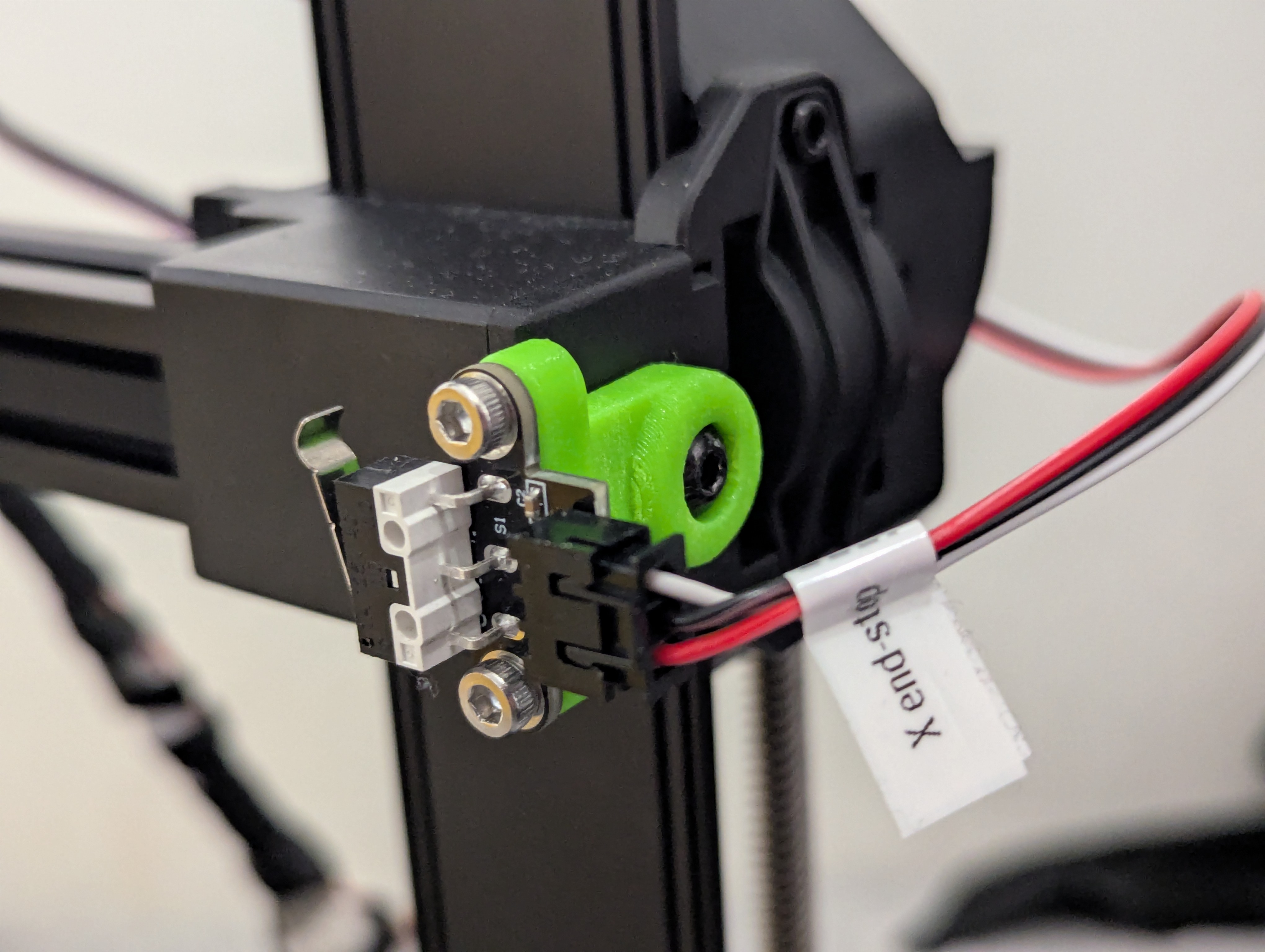
Step 11: Install C-axis drive system
C-axis pulley, stepper and drive installation
- Install C-driven-pulley in carriage mount
- Add optical sensor to carriage mount for C-axis position sensing
- Mount C-axis (yaw) stepper motor to carriage mount using 4x M3x6mm bolts
- Use long hex key to access stepper motor mounting bolts
- Install GT2 timing belt connecting stepper motor to C-driven-pulley
- Tension belt properly - should be snug but not over-tensioned
- Route slip ring wires through the C-driven-pulley center hole
- Connect C-axis stepper directly to control board (not through slip ring)
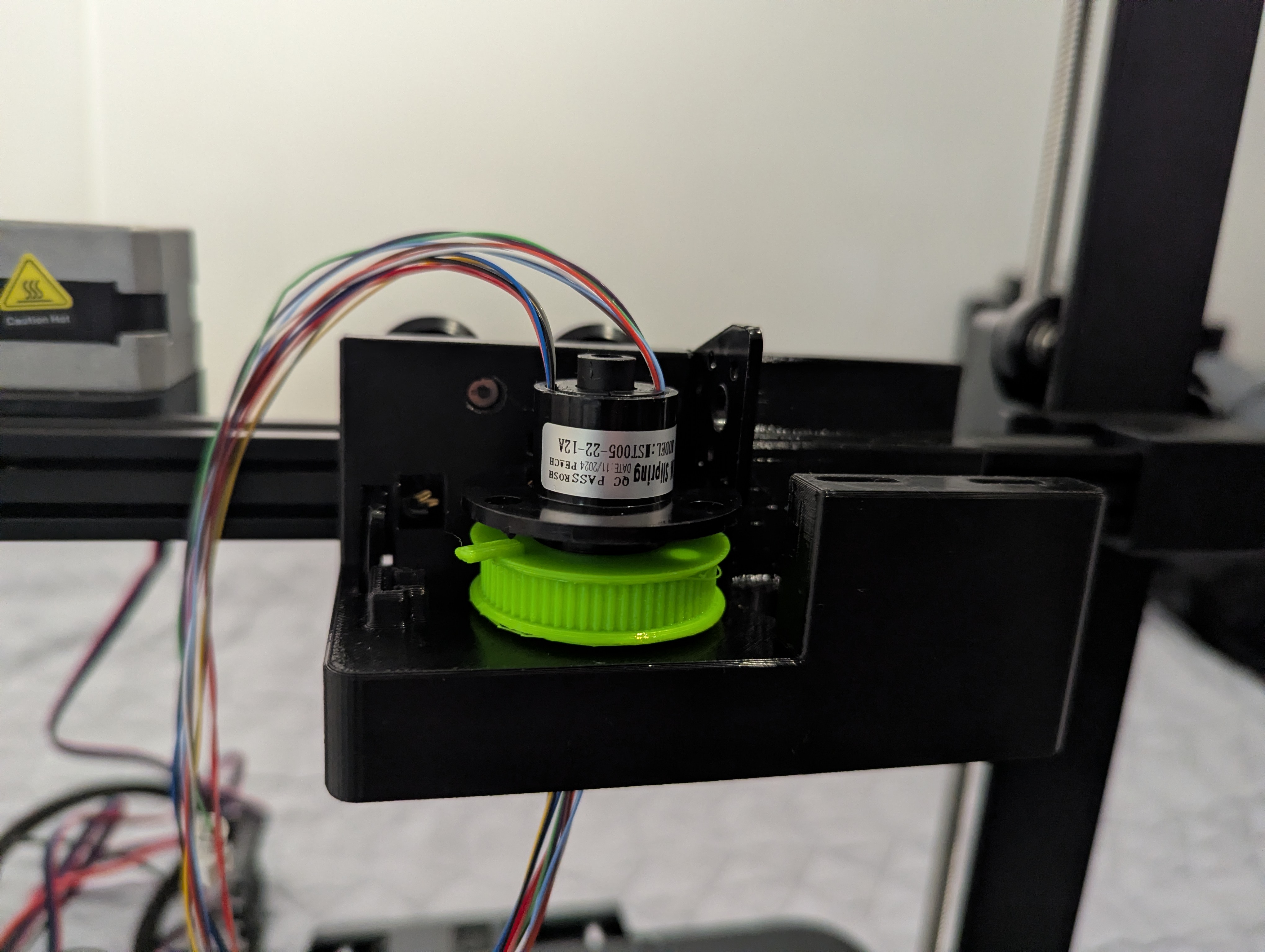
Figure 8: C-driven-pulley installed in carriage mount

Figure 9: Complete C-axis installation with stepper motor and belt
Step 12: Install B_arm and connect wiring
B_arm installation and wire routing
- Route all wires and Bowden tube through B_arm center
- Attach B_arm to carriage mount using 2x M3x10mm bolts
- Verify clearances - Both C and B axes should move freely
- Test mechanical limits - Check rotation range without collisions
- Secure wire routing - No pinching or interference during motion
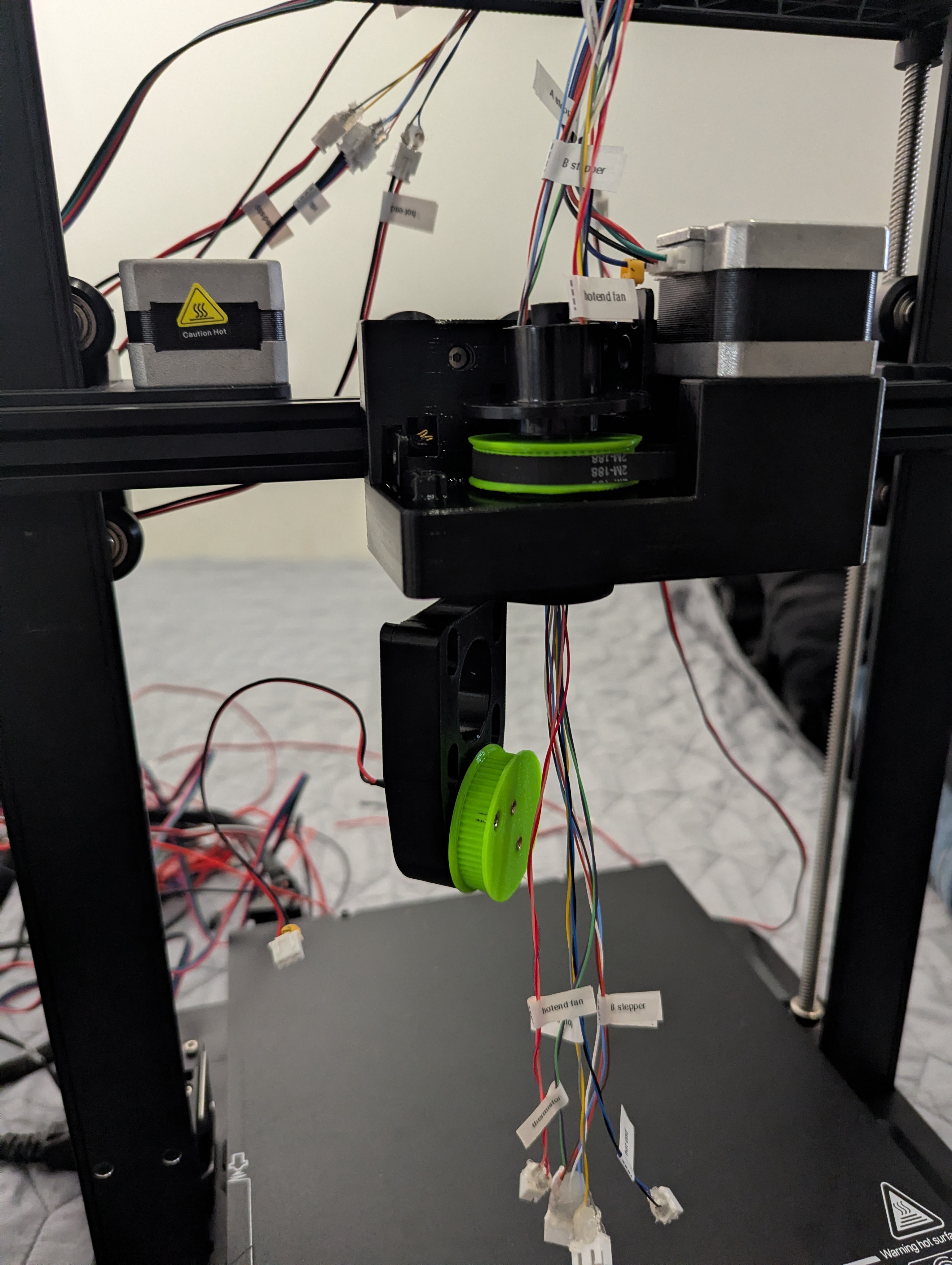
Figure 10: B_arm connected to carriage mount with proper wire routing
Step 13: Install B-axis drive system
B-axis drive system installation
- Install B-axis (tilt) stepper motor to B_arm mounting points
- Install GT2 timing belt connecting B-axis stepper to b-driven-pulley
- Tension belt properly - should be snug but allow smooth rotation
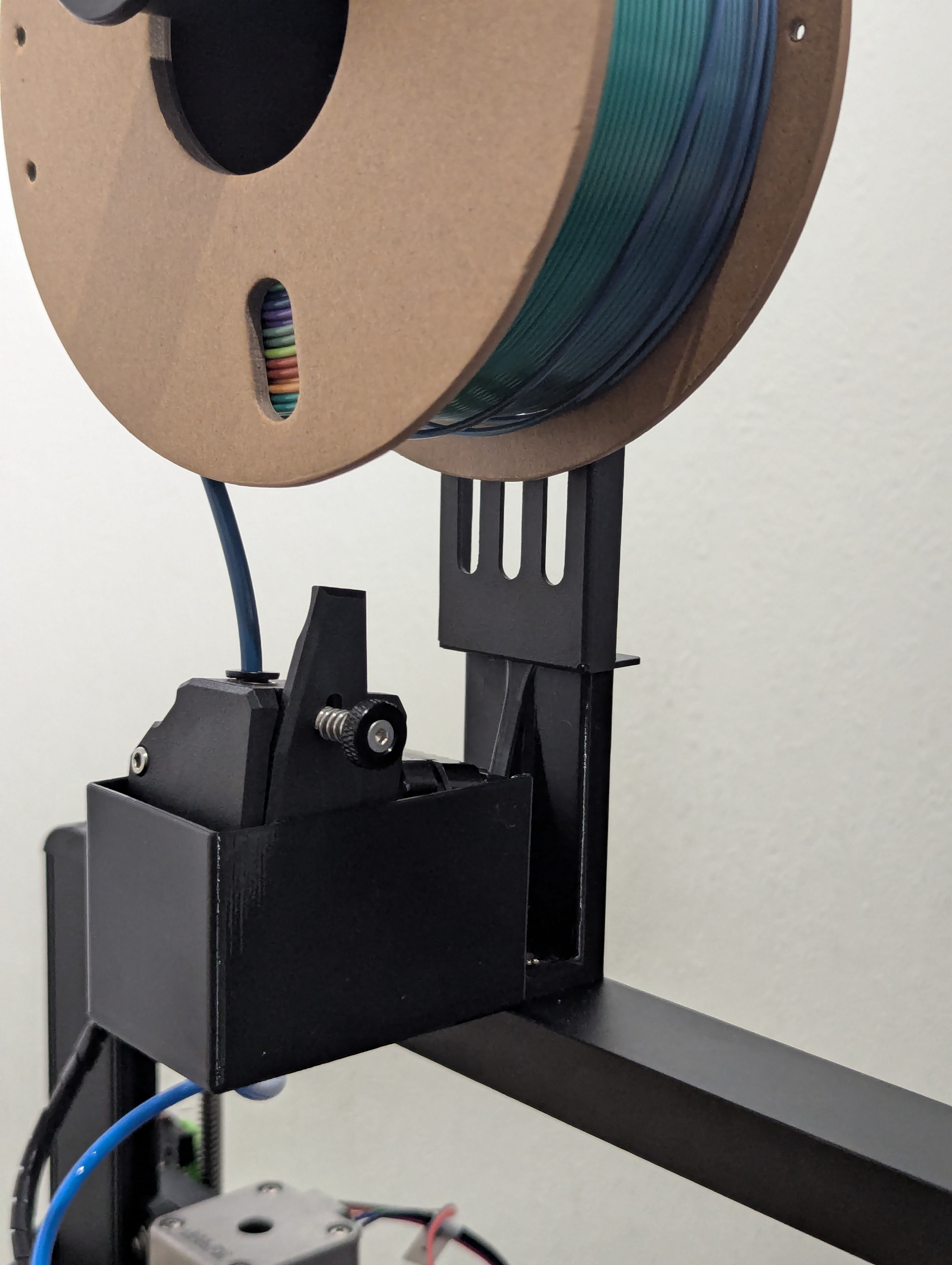
Step 14: Install hotend and final wiring
Hotend installation and complete wiring
- Attach hotend assembly to B_arm mounting points
- Connect all hotend components through slip ring connections:
- Hotend heater (2-pin connection)
- Hotend thermistor (2-pin connection)
- Hotend cooling fan (2-pin connection)
- Connect B-axis stepper through slip ring (4-pin connection)
- Connect B-axis endstop through slip ring (2-pin connection)
- Check slip ring rotation - should rotate freely without binding wires
Cable management
- Organize all wiring for clean routing
- Secure loose cables to prevent interference
- Test full motion range with all cables connected
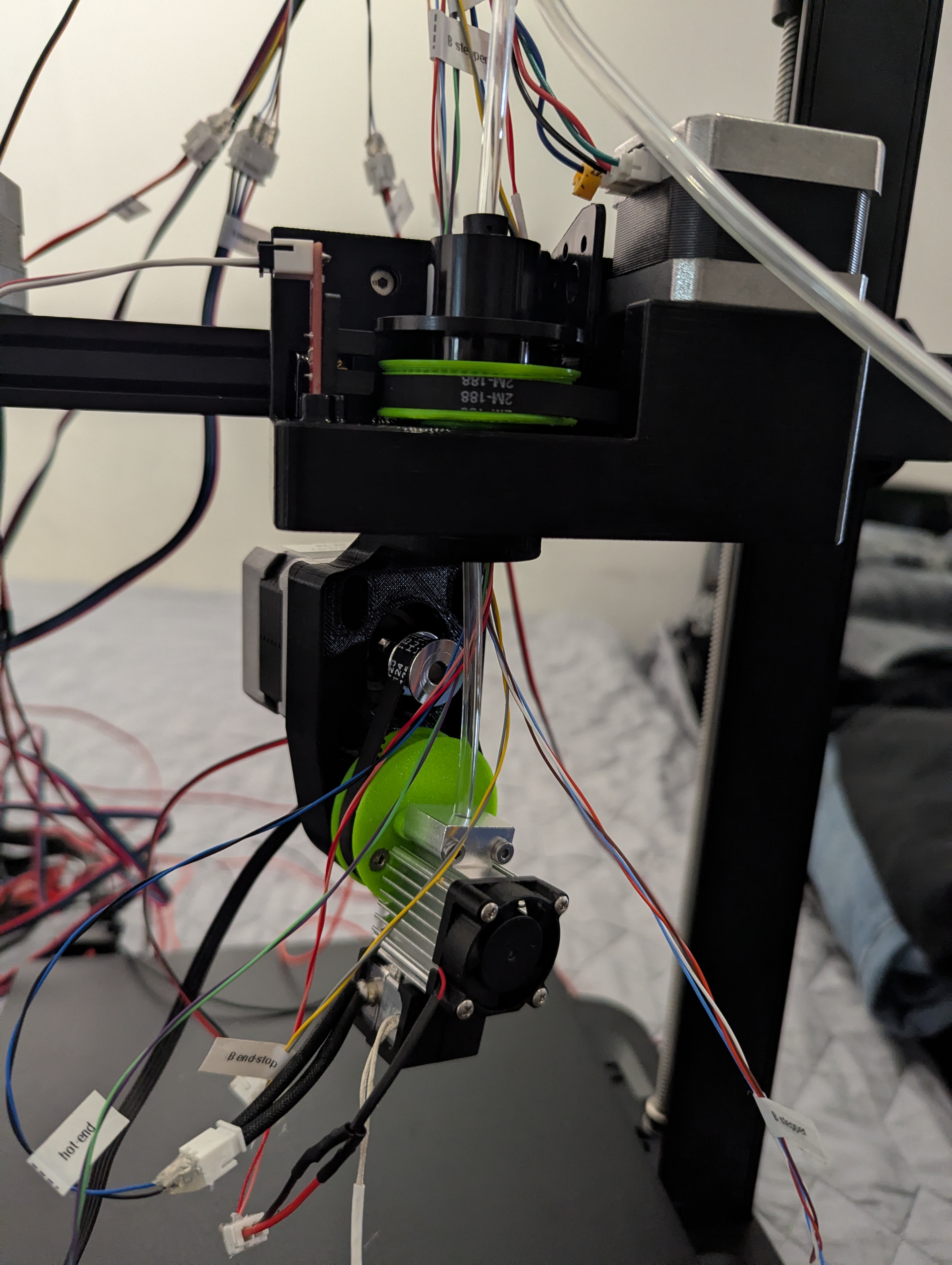
Figure 11: Complete assembly with all components connected (before cable management)
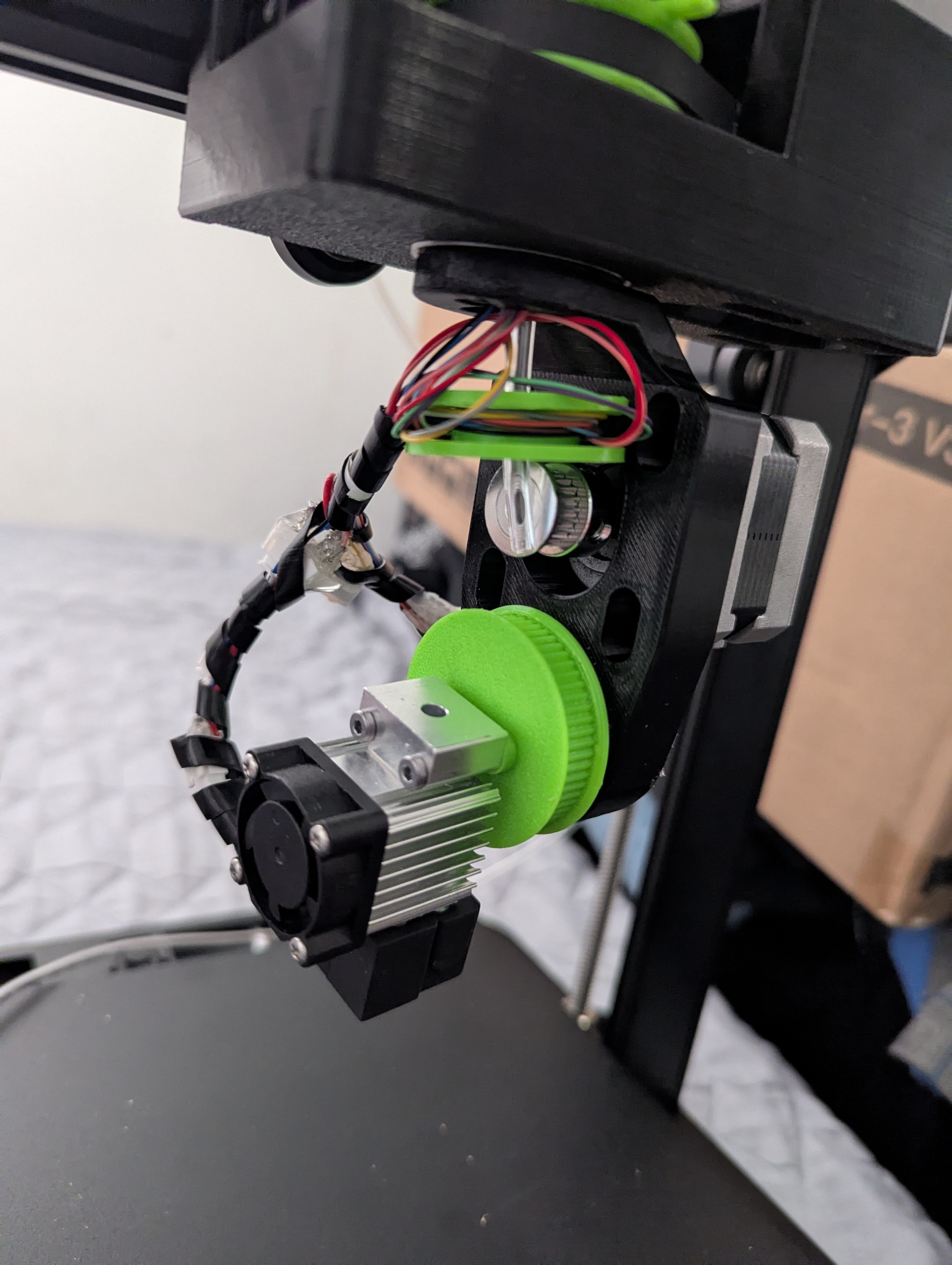
Figure 12: Same assembly with cable management in progress
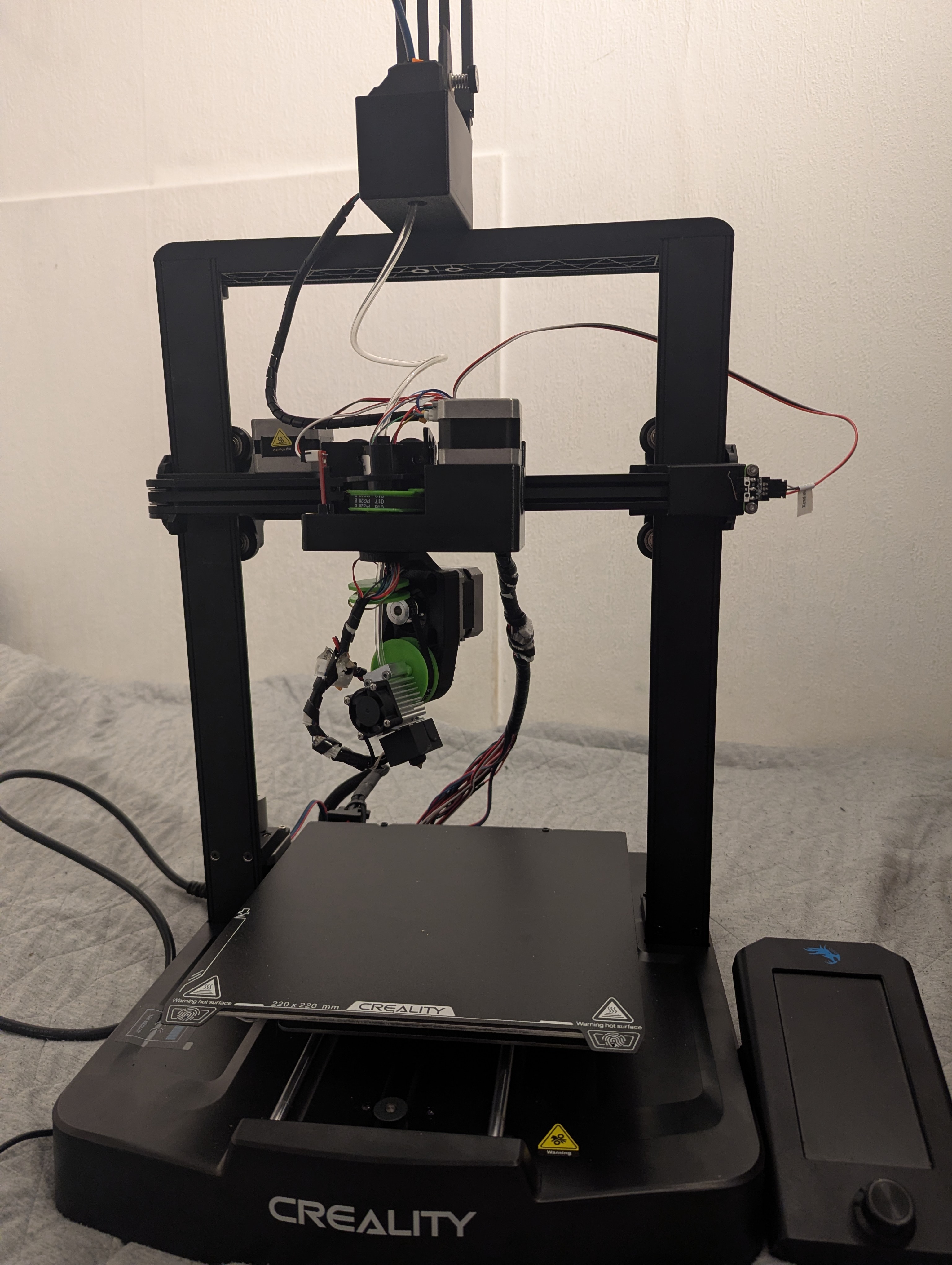
Figure 13: Completed Rep5x 5-axis printer ready for calibration
Note: Improved cable management photos coming soon - this build was done with limited cable organizers.
Part 4: Testing and calibration
Step 15: System verification and testing
System verification
- Power up system and verify no error messages
- Test all 6 axes with careful manual G-code commands:
- X, Y, Z axes:
G1 X10 F1000(move slowly, verify direction) - C-axis:
G1 C45 F1000(rotate in 45° increments) - B-axis:
G1 B10 F1000(tilt slowly, watch for collisions) - Extruder:
G1 E10 F100(extrude 10mm slowly)
- X, Y, Z axes:
- Verify endstops trigger properly with
M119command - Check thermal systems:
- Hotend heating:
M104 S200(heat to 200°C) - Bed heating:
M140 S60(heat to 60°C) - Verify temperature readings are stable
- Hotend heating:
Extruder calibration
Why calibrate the extruder:
- Incorrect E-steps leads to over/under-extrusion, poor print quality
How to calibrate E-steps:
- Mark filament - Make a mark 120mm above the extruder entrance
- Heat hotend -
M104 S200(or your printing temperature) - Extrude 100mm - Send command:
G1 E100 F100 - Measure remaining distance - Measure from extruder entrance to your mark
- Calculate actual extrusion - Should be 20mm remaining (120mm - 100mm)
- Calculate new E-steps:
- If more than 20mm remains → extruding too little
- If less than 20mm remains → extruding too much
- Formula:
New E-steps = (Current E-steps × 100) / Actual distance extruded - Example: Mark is at 25mm instead of 20mm → only 95mm extruded
- New E-steps = (Current × 100) / 95
- Update firmware -
M92 E[new value]thenM500to save - Verify - Repeat test to confirm accuracy
5-axis kinematic calibration
- Use Rep5x calibration tool at calibrator.rep5x.com
- Follow cone or camera-based calibration procedure:
- Cone method: Print calibration cone and measure deviations
- Camera method: Use computer vision to detect tool center point offset
- Update firmware with calibrated kinematic parameters:
- C-axis offset
- B-axis offset
- Tool center point (TCP) coordinates
- Test print simple geometry to verify functionality
Assembly complete! Your Rep5x 5-axis conversion should now be ready for calibration and first prints. Join our Discord community for support and to share your successful build!
Note: Detailed printer-specific assembly instructions are being written. Please follow the universal instructions above and refer to the printer-specific BOM for additional components needed.